“Why is my Lighthouse Score low?” 7 tips from a web dev
In this article, I’ll share key factors affecting your Lighthouse Score and will provide actionable tips to improve your site’s performance and boost your rankings.
Written by Tomas Vorel

In this article, I’ll share key factors affecting your Lighthouse Score and will provide actionable tips to improve your site’s performance and boost your rankings.
Written by Tomas Vorel

If you’re wondering why your Lighthouse Score is low, you’re not alone. Many web developers and content professionals face this challenge, especially when dealing with marketing websites where page speed, user experience, and SEO play a crucial role. Let’s dive into a few key factors affecting your Lighthouse Score and explore actionable solutions to improve it.
One of the most common reasons for a low Lighthouse Score is slow loading speed. The good news? There are several ways to optimize your website for faster load times.
Unoptimized assets can significantly slow down your site, impacting both user experience and search rankings. This is where efficient file formats like WebP become invaluable. WebP offers powerful compression capabilities that reduce file sizes substantially compared to traditional formats like JPEG or PNG, all without sacrificing image quality.
WebP has additional advantages, including support for lightweight animated images—something PNG lacks, as it’s limited to static images. Both formats are widely compatible with major browsers, but WebP has gained increasing support across Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Opera, while PNG continues to offer universal compatibility across all platforms.
Beyond choosing the right format, it's important to optimize and properly size your assets. Services like TinyPNG can help with basic image compression. Additionally, avoid using overly large images, like a 4K image for a card header, as this can unnecessarily increase load times. With efficient compression, WebP can significantly reduce loading times while maintaining visual fidelity (for example, the WebP image below is only 17 kB).
Third-party services and scripts can be invaluable for adding functionality, insights, and interactive features to your site. But they also come at a cost. Many of these scripts, often implemented via tools like Google Tag Manager (GTM), allow marketers to insert useful tools like Intercom or Hotjar without needing to involve developers. This flexibility is convenient, but it can quickly accumulate to hundreds of kilobytes or even megabytes of additional data, bogging down your site’s load time and impacting your Lighthouse Score.
Each third-party script that loads immediately competes for resources, slowing down how quickly your main content appears on the screen. To counter this, prioritize using Defer and Async attributes where possible. When set on non-critical scripts, Defer will load the script after the HTML is fully parsed, and Async will download the script alongside HTML parsing, only executing it once it’s ready. Both parameters ensure your core content loads first, which enhances user experience and maintains a cleaner, faster performance profile.
For an even finer control, assess which scripts are truly necessary and consider alternatives or combined solutions to reduce redundancy. If you use GTM, create rules to load scripts only on specific pages where they’re required, which limits the performance impact on your entire site.
A bundle analyzer is a tool that helps you visualize what’s inside your final bundle (I mean the complete package of files delivered to the end user when they load a webpage or app). It’s especially helpful for pinpointing which parts of your code are adding the most to the bundle’s file size.
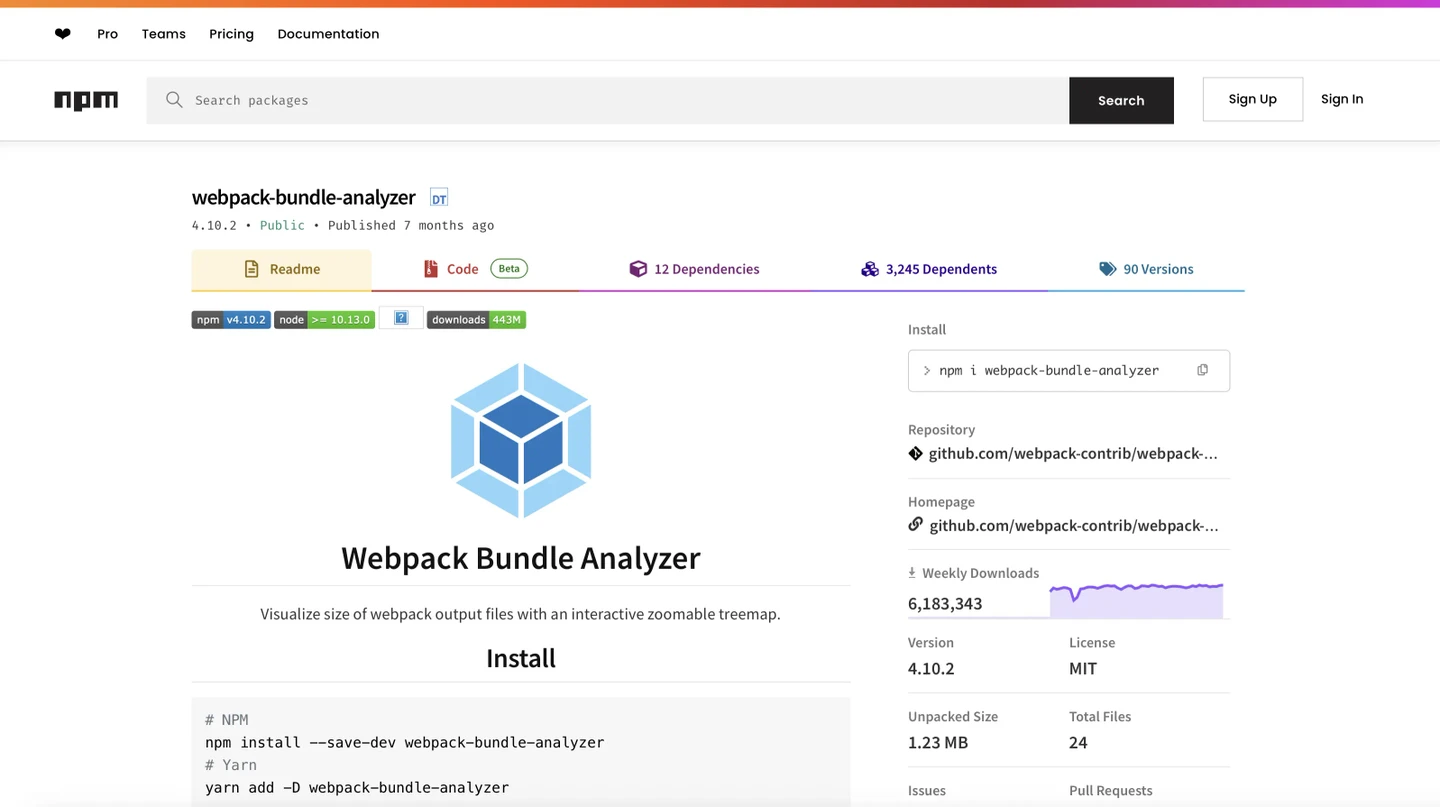
I’m going to provide a specific example: When you’re developing a website, you typically use npm (Node Package Manager) to include various libraries and packages to help with different functionalities. For example, you might need Moment.js, a popular library used to parse, manipulate, and format dates and times. You could use it to format a UTC timestamp (like the one you get from Kontent.ai) into a more user-friendly format, such as displaying it as “Feb 24, 2025.”
The problem with libraries like Moment.js is that they can be quite large in terms of file size. When these packages are included in your project, they increase the overall size of your bundle. Larger bundles take longer to load, which can slow down your website or web app.
This is where the bundle analyzer comes in handy. It helps you:
If you’re working on a static marketing site, using minimal JavaScript is key. You don’t need JavaScript to render HTML or CSS, so overloading your site with unnecessary scripts will only slow it down. One solution is to adopt the island architecture approach, which can be efficiently implemented with frameworks like Astro.
In this model, static content is prioritized, and only specific components—like forms or pop-ups—use JavaScript. By isolating JavaScript to where it’s really needed, you minimize the load and improve your Lighthouse Score.
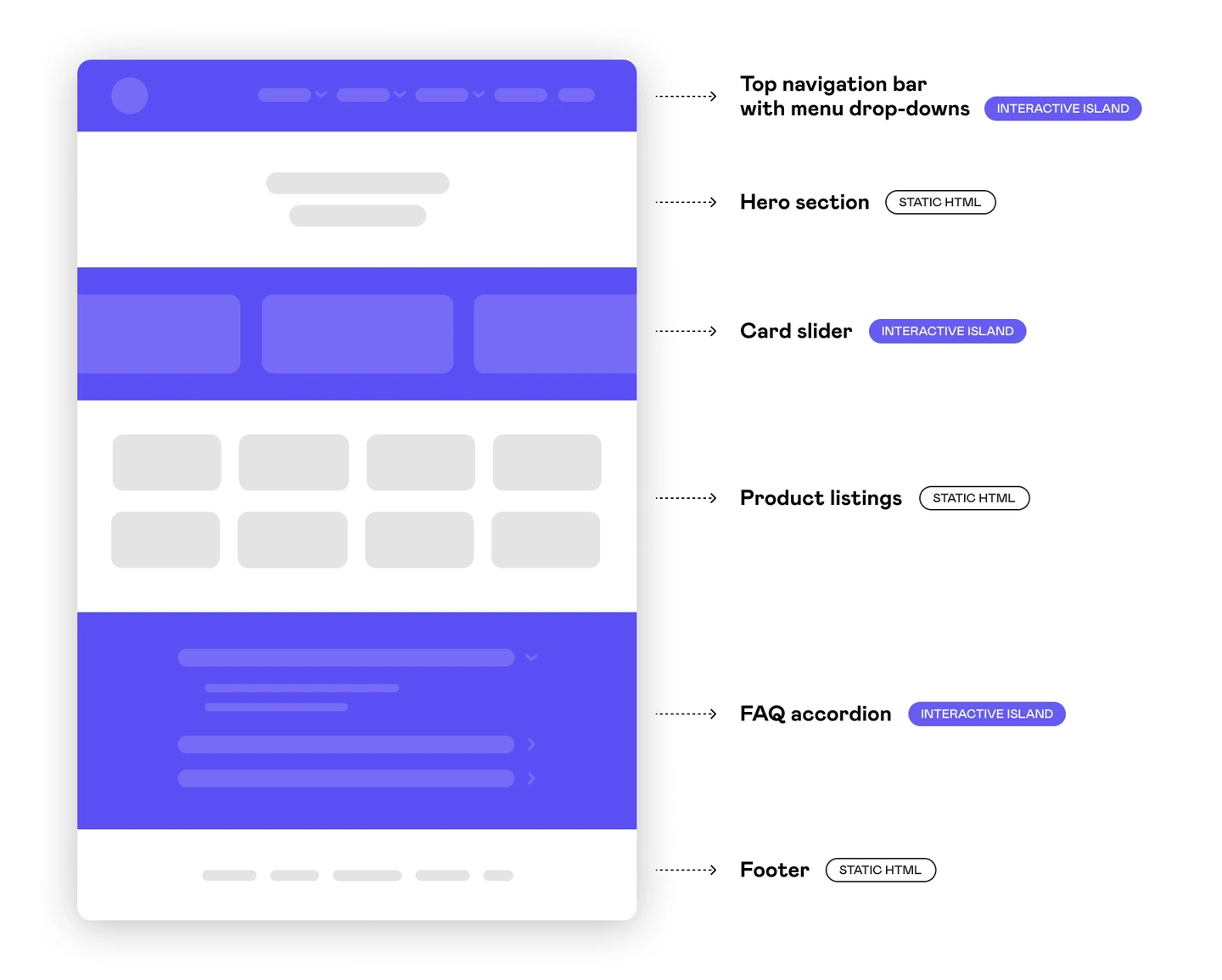
When working with complex web applications that feature a lot of interactive components, such as registration forms, modals, or pop-ups, you can improve performance by using dynamic imports. This approach ensures that only the necessary code is loaded when it’s actually needed, rather than on the initial page load.
For example, imagine you have a registration form hidden behind a modal. By default, when a user visits the page, the code for the form (including all its fields) is downloaded, even if the user doesn’t click to open the modal. This means that the page load time increases because it’s fetching code that the user may not interact with right away.
With dynamic imports, the code for that form will only be loaded when the user clicks the button to open the modal. This can significantly reduce the initial load time of your web app, as you’re not downloading unnecessary code upfront.
I tried to optimize our site using dynamic imports, which reduced JavaScript load time by several seconds, but our new Lighthouse Score was lower than before due to significant layout shifts. Layout shift happens when elements on a webpage suddenly move or “jump” as the page loads, creating a jarring experience for the user. This is considered a bad user experience and, as I've described, can significantly lower your Lighthouse Score.
One common cause of layout shift is the loading of large images or other heavy assets. If an image doesn’t have a designated space reserved while it’s loading, it can force other elements to move when it finally appears.
To prevent layout shifts, it’s essential to reserve space for images and content as they load. One effective solution is to use skeleton UI—placeholder elements that mimic the structure of the final content. Skeletons can keep the layout stable while the content is fetched, allowing for a smoother experience from the moment the page starts loading. Tools like Next.js offer built-in image optimization with transparent placeholders to reserve space, maintaining a consistent page layout and avoiding unexpected jumps.
As you navigate these optimizations, it’s important to think holistically about your website’s performance, especially when it comes to your Lighthouse Score. For marketing websites, a high Lighthouse Score is crucial because it directly affects SEO, influencing how your site ranks in search results and ultimately driving organic traffic. But if you’re working on applications where users primarily come to perform tasks or work, the emphasis on SEO is less critical. In these cases, focusing on Lighthouse metrics may not yield the same benefits. Instead, prioritize a seamless user experience that supports your users’ goals.
To improve your site’s performance and Lighthouse Score, consider these essential strategies:
Defer and Async attributes for non-critical scripts to ensure main content loads faster, and limit scripts to pages where they’re essential.
What if we told you there was a way to make your website a place that will always be relevant, no matter the season or the year? Two words—evergreen content. What does evergreen mean in marketing, and how do you make evergreen content? Let’s dive into it.
Lucie Simonova

How can you create a cohesive experience for customers no matter what channel they’re on or what device they’re using? The answer is going omnichannel.
Zaneta Styblova

To structure a blog post, start with a strong headline, write a clear introduction, and break content into short paragraphs. Use descriptive subheadings, add visuals, and format for easy scanning. Don’t forget about linking and filling out the metadata. Want to go into more detail? Dive into this blog.
Lucie Simonova