Use sitemaps to improve SEO and accessibility
When coming to your website, search engines first check whether you provide a sitemap. If you do, they primarily index the pages you list in the sitemap file.Sitemaps are particularly important for large websites with hundreds of pages because search engines might not index some recently created pages.
Improve SEO with sitemaps
There are two kinds of sitemaps. Sitemaps for people and sitemaps for search engines. Sitemaps for people help your website visitors understand the structure of content your website has. These sitemaps improve your website's accessibility because they help your visitors find the content they're looking for more easily. In the video below, one of our customers, heycar
A sitemap for search engines contains an unstructured list of pages on your website. Provide such a sitemap to ensure good SEO – if a search engine finds what your potential visitors search for, they can find it using the search engine and become real visitors.
A sitemap for search engines is an XML file that contains a list of URLs that doesn't reflect the hierarchy of the site's content.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.example.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<url>
<loc>https://www.mywebsite.org/home</loc>
<lastmod>2020-01-08</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://www.mywebsite.org/shops</loc>
<lastmod>2020-02-14</lastmod>
<changefreq>weekly</changefreq>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://www.mywebsite.org/shops/brisbane</loc>
<lastmod>2020-03-07</lastmod>
<changefreq>weekly</changefreq>
</url>
</urlset>Help people understand your website structure
A sitemap for people is a webpage that shows the structure of your website. It improves accessibility as it helps visitors better orient themselves in the content you provide. It’s especially useful in the case of complex websites with nested categories and pages. For instance, a company website with pages for shops across multiple cities, catering services, and a list of the company suppliers might have a website with the following structure:Ways to build sitemaps in Kontent.ai
You can model a sitemap for your Kontent.ai project using linked content items or taxonomy. You can build both types of sitemaps with either approach, but you should first decide whether you want to build a sitemap for search engines or a sitemap for your visitors (or both). To build a sitemap for search engines, it's best to use the taxonomy approach as it's easier to manage the flat structure with it. You can use either approach to build a sitemap for people. However, when you use the taxonomy approach, you also give your content creators an easy way to find the tagged content and see your website structure in Kontent.ai.Create sitemaps using linked content items
Sitemaps for visitors
When building a sitemap for your visitors, you need to link your content items in a way that reflects the hierarchy of your website. With this approach, you always go from the top of your website's hierarchy. Take the highest content item and link to it the items directly below. Then continue the same way with all the items lower in the hierarchy.Sitemaps for search engines
If you want only a sitemap for search engines, you don't need to reflect your website's structure. Take the highest content item and link to it all the lower items you want in the sitemap. However, we suggest you use the taxonomy approach in this case because it's easier to manage the flat structure with it.1. Adjust the content model
You need to adjust the content types of items you'll link to items lower in the hierarchy.- In
Content model, open the content type you want to update.
- Insert the Linked items element.
- Name it Sitemap items.
- (Optional) Restrict the element to accept only content types of items lower in your website hierarchy.
- (Optional) Add a helpful guideline to explain the purpose of the element.
- Click Save changes.
2. Link the content items
Now you have your content types ready and you can link the content items according to what you're building. If you're creating a sitemap for search engines, open the highest content item with the Sitemap items element. Then link to it all the lower items you want in the sitemap. If it's a sitemap for people, go from the top of the hierarchy and link the items that are one level lower. If you were building a sitemap for the website in the schema above, you'd create a hierarchy similar to this: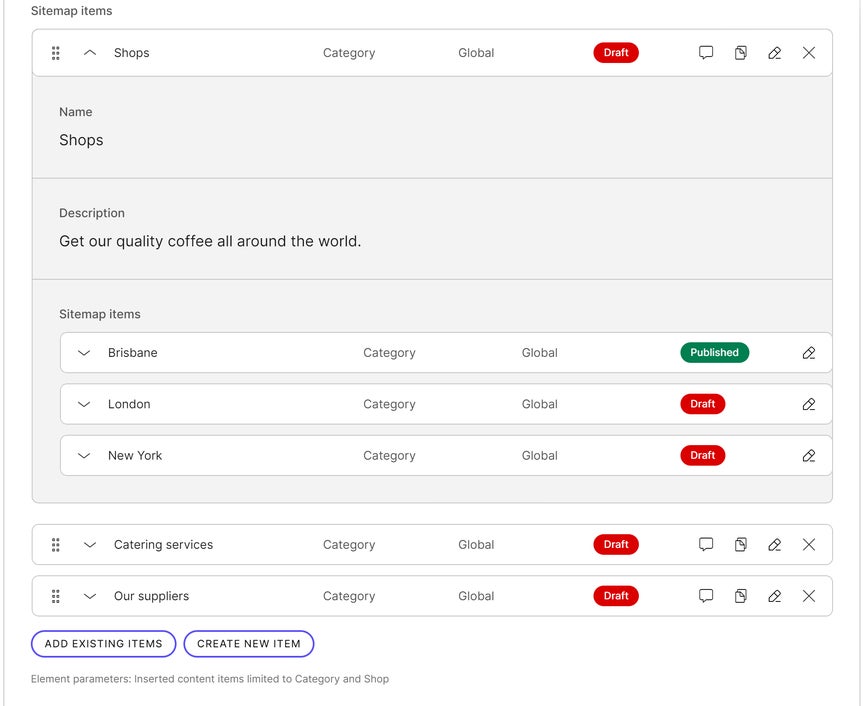
3. Build the sitemap in your app
After you publish the content items, your app needs to retrieve the items using the Delivery API to build the sitemap.With the Delivery GraphQL API, get the item highest in your website hierarchy and query the items linked in its Sitemap items element.
query GetSitemapItems {
landingPage(codename: "landing_page") {
sitemapItems {
items {
title
url
}
}
}
}
Sitemaps for visitors
In the case of a sitemap for people, we suggest using thedepth=1 parameter to include linked items only one level below. This helps you to keep track of what level of the sitemap you’re on when you process the responses from the API.
To get the full hierarchy, use the call above for every item on each level. Save the title, URL, and position in the hierarchy of every item you get. This way you’ll progressively get to the bottom of your website’s hierarchy.
After you get all the items you want in your sitemap, you can start building the sitemap in your app using the data you’ve retrieved.